Our Performance
This research proposes an innovative quantitative trading framework, LLM-MAS-DRL (Large Language Model - Multi-Agent System - Deep Reinforcement Learning), which integrates the semantic understanding capabilities of large language models, the collaborative decision-making mechanisms of multi-agent systems, and the adaptive optimization capabilities of deep reinforcement learning. The system employs five specialized agents (Fundamental Analyst, Sentiment Analyst, Industry Trend Analyst, Market Risk Analyst, and Black Swan Event Detector) for collaborative analysis, coordinating conflicts and information integration among agents through a Model Context Provider (MCP) mechanism, and optimizing trading decisions using the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm.
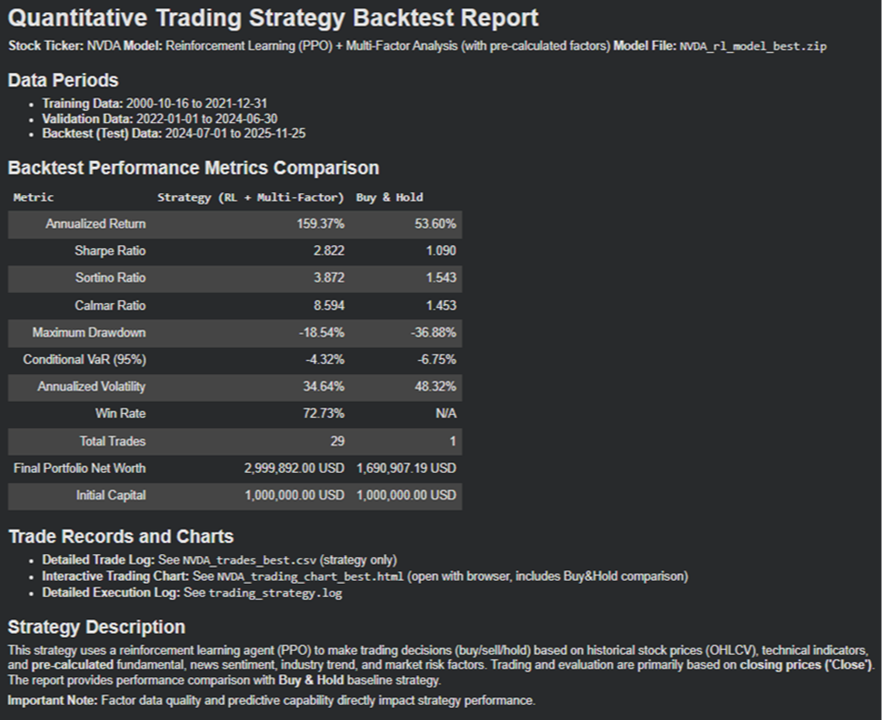
The empirical study targets five US-listed stocks (NVDA, AAPL, MSFT, BAC, AMZN), spanning 25 years of historical data from 2000 to 2025, strictly divided into training period (2000-2021), validation period (2022- June 2024), and out-of-sample testing period (July 2024-June 2025). Results demonstrate exceptional performance during the extreme market volatility testing period, with average annualized return of 53.87%, Sharpe ratio of 1.702, and maximum drawdown of only 12.54%, significantly outperforming the buy-and-hold strategy (annualized return 26.08%, Sharpe ratio 0.765, maximum drawdown 30.24%). Comprehensive comparisons with nineteen baseline models confirm the framework’s superiority, including traditional machine learning models (ARIMA, Logistic Regression, SVM, Random Forest, XGBoost), deep learning models (LSTM, Bi-LSTM, Transformer), and other deep reinforcement learning algorithms (TRPO, DQN, DDPG, SAC).
Ablation studies reveal component contributions:the Industry Trend Agent is most critical to system performance (removal decreases annualized return by 18.70 percentage points), the Fundamental Agent provides stability (Sharpe ratio contribution of 0.310), and the Black Swan Agent offers important protective value (maximum drawdown reduction of 7.3 percentage points). This research confirms the effectiveness, robustness, and scalability of the LLM-MAS-DRL architecture in complex financial environments, providing significant methodological innovation for quantitative trading and financial technology domains.